Introduction
Since someone I know was hacked, it was decided to create an article that would be geared more towards newbies coming into both cryptocurrency and web surfing.
I have quite a lot of experience with various types of hacks and viruses in the past, which is why I can give a lot of useful advice based on my experience. The article will cover topics such as:
- What is WEB1, WEB2, WEB3
- Definition of viruses and their species
- Types of hacking
- Safety tips in WEB

What is WEB1, WEB2, WEB3?
Web 1, Web 2 and Web 3 are terms that describe the stages of development of the Internet and related technologies.
What is important: although there are three stages, there is no strict boundary between them. That’s because the evolution of the web is slow.
Something disappears, something stays, and something changes. Therefore, there is no exact date when, for example, the Web 1 era ended and Web 2 began. Everything is conditional.
And now I will tell you more about each stage.
WEB1
Web 1, also known as “static web” or “read-only” is the first era of Internet development. During Web 1.0, websites were static bulletin boards, threaded forums, and personal pages. People visited them to read text and look at pictures.
Other than links, there were no other interactive elements on the sites. Commenting, online polls, uploading user files or creating personal accounts were out of the question. Picture below shows an example WEB1 website very well.

A group of people – webmasters – worked on creating and maintaining websites. They decided what content to publish, how often, and in what format. Other users acted as passive consumers of information.
They built sites using HTML markup without JavaScript, which gave sites dynamism. And all because the Internet in those years was slow and loading scripts would not have pulled.
This is what can be attributed to the features of sites of the Web 1 era:
- Updated manually by webmasters
- Designed for one-way communication. That is, users could only read content, but not interact with it.
- Had simple design and limited visual appeal. They were built on simple layouts with monochrome backgrounds and primitive navigation.
- Had no personalization. All visitors saw the same content, individual preferences and interests were not taken into account.
- There was no social media. There was no place to create profiles, get followers and share content.
WEB2
Web 2, also known as the “dynamic web” or “social web”, is the next stage in the development of the Internet. It began in the late 1990s and continues to this day.
The term “Web 2” was first used by web designer and user experience expert Darcy Dinucci in 1999. However, it became popular after a conference dedicated to Web 2 in 2004 in San Francisco.
Modern Web 2 is a network of interactive websites and platforms where content is created by users rather than by administrators and resource owners.
Typical representatives of the era are Face Social Network, YouTube, Twitter, TikTok and Telegram. Their common feature: focus on user-generated content and social interaction. Picture below shows an example WEB2 website very well.
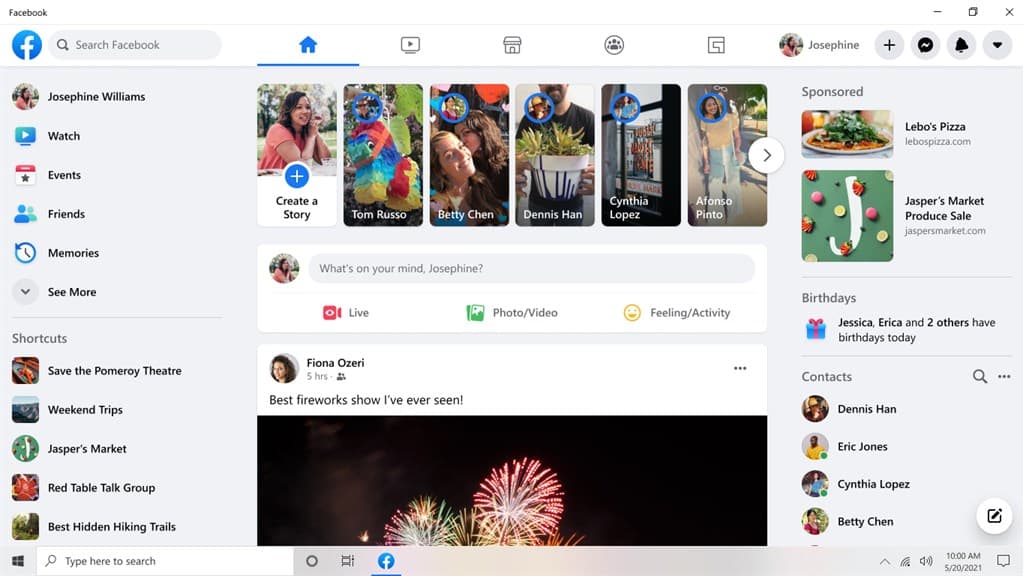
This is what can be attributed to the features of sites of the Web 2 era:
- User-generated content. Anyone on the internet can create content and share it with others
- Social networks. Emerged with Web 2.0 and became platforms for users and businesses to communicate and share information
- Collective Intelligence. This is when different users can evaluate, comment and edit content together (example – Wikipedia).
- Interactivity. User interfaces have become more complex and interesting.
- Cloud technologies. Users and businesses were able to store, process and share data with each other over the internet anywhere in the world and through any device
- Personalization and recommendations. Recommendation algorithms emerged and began offering users content that took into account their interests, habits and buying behavior
- Mobility. Applications, services and platforms became adapted for mobile devices. No longer did you have to sit in front of a computer to go online.
- Authorization. It became possible to create an account on virtually any site. Users began to leave their personal data in exchange for convenience and the ability to use resources. And businesses used them for their own purposes, for example, to sell them to advertising agencies
WEB3
Web 3, also known as the “semantic web” or the “intelligent web”, is the next stage in the development of the web that has not yet arrived, but web developers and IT corporations are already working on it.
The challenge at hand is to create a new version of the web that is more intelligent and automated. That is, to develop the web’s ability to:
- Understand the meaning of the content displayed
- Understand user requests, which they make by text, voice or otherwise
- Maximize the adaptation of content to each user individually
In other words, the Internet in the era of Web 3 will become more like a live interlocutor than a machine.

Web 3 should be based on the following technologies:
- Artificial intelligence (AI): Creates intelligent systems like ChatGPT or Bard that can predict and respond to user queries like a live interlocutor
- Distributed Registries: And to put it simply, blockchain. It allows the creation of decentralized and reliable data storage systems that can be used for various purposes, such as cryptocurrencies
- Cryptography: Encryption technology provides security and confidentiality of data and allows for authentication and integrity of information. Used to create digital signatures and encrypt data
- Decentralized applications: Operate based on smart contracts and utilize distributed registries. Run on decentralized networks. As a result, users have more control over their data
- Metadata: Special markup that tells algorithms what a page is about. An algorithm, using metadata, understands the context establishes logical connections between pieces of information and makes associations similar to what humans do
Definition of viruses and their species
What is virus?
This is a type of malware that is capable of spreading its copies to infect and corrupt data on the victim’s device. Viruses can enter a computer from other already infected devices, through storage media (CDs, DVDs, etc.), or through the Internet network.
Today, there are different types of computer viruses, differing in their main method of spreading and functionality. While viruses were originally spread on floppy disks and other media, viruses spreading via local and global networks (Internet) are now dominant. The functionality of viruses, which they adopt from other types of programs, is also growing. Currently, there is no unified system for classifying and naming viruses, which is why in this article I will describe them by their malicious functionality.
Also, there are so many viruses that it would be impossible for me to describe each of them in an article, and most of the time everything that spreads on a computer can also be infected on a phone, which is why I will not touch on this topic
Stealer
Stealer is a type of malware designed to steal sensitive information from an infected device. Quite common way to hack people nowadays, if before these viruses steal only saved data, now they can get much more important information:
- Logins and passwords from various accounts (social networks, mail services, banking systems, etc.)
- Credit and debit cards
- Personal documents and data
- Browser information, including history, cookies and stored credentials
- Cryptocurrency wallets
Next, I will show an example of what information this virus can obtain about a person.

As you can see in the photo, after opening the virus, the attacker received a screenshot of the screen at the time of the opening.

Also, here’s an example of the kind of data an attacker can get if you open their file. In addition to this comes cookies, with which he will be able to access almost any site you have been logged into.
RAT (Remote Access Trojan)
A Remote Access Trojan (RAT) is a type of malicious software (malware) that allows a cyber attacker to gain unauthorized access to a victim’s computer or network. RATs are used to remotely control the infected system, enabling the attacker to carry out various activities without the user’s consent. Simply put, an attacker can do almost anything they want to your computer, for example:
- Remote Control. Attackers can remotely manage and control the infected system, as if they were physically present
- Data Theft. RATs can be used to steal sensitive information such as login credentials, financial data, personal documents, and other confidential information
- Keylogging. They often include keylogging functionality, recording every keystroke made by the user to capture passwords and other critical data
- Screen Capture and Webcam Access. RATs can take screenshots, record video, and capture audio from the infected system
- File Transfer. They enable the attacker to upload and download files from the infected system
- Network Surveillance. RATs can monitor network traffic and capture data packets for analysis
- Software Execution. They can execute other malicious programs or commands on the infected machine

Here you can see an example of one such virus, as well as the features an attacker can pull off on your computer
Worm
A computer worm is a type of Trojan that is capable of propagating or replicating itself from one system to another. It can do this in a number of ways. Unlike viruses, worms don’t need a host file to latch onto. After arriving and executing on a target system, it can do a number of malicious tasks, such as dropping other malware, copying itself onto devices physically attached to the affected system, deleting files, and consuming bandwidth.

In this photo, you can see an example of an infected device that continues to spread the virus it has received.
Clipper
Clipper malware, also known as a “clipper” or “clipboard hijacker,” is a type of malicious software designed to monitor and manipulate the contents of a computer’s clipboard. This type of malware specifically targets clipboard data to intercept and alter information, often to steal cryptocurrency or other sensitive information.

Here you can see the algorithm of the clipper. Nowadays they are able to replace almost any important data you can think of: various links (e.g. steam trade link), crypto wallets (Bitcoin, Ethereum, Monero, Bytecoin, Litecoin, etc.), various wallets and other data.
Ransomware
Ransomware is a malware designed to deny a user or organization access to files on their computer. By encrypting these files and demanding a ransom payment for the decryption key, cyberattackers place organizations in a position where paying the ransom is the easiest and cheapest way to regain access to their files. Some variants have added additional functionality – such as data theft – to provide further incentive for ransomware victims to pay the ransom.


In these two pictures you can see an example of this virus. You will not have access to your computer other than this window.
Botnet
Botnet malware refers to a type of malicious software that infects a network of computers, turning them into “bots” or “zombies.” These compromised systems, collectively known as a “botnet,” are remotely controlled by a cybercriminal, often referred to as a “botmaster” or “herder.” Botnets are used for various malicious activities, leveraging the combined power of multiple infected machines to amplify their impact.

Infected computers can be compromised with their various uses:
- Remote Control. The botmaster can control the botnet remotely, issuing commands to the infected machines without the knowledge of their owners
- Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks. Botnets are often used to launch DDoS attacks, overwhelming a target website or server with traffic to render it inaccessible
- Spam Distribution. Botnets can be used to send massive amounts of spam emails, often as part of phishing campaigns to distribute additional malware or scam users
- Data Theft. Botnets can be used to steal sensitive information, such as login credentials, financial data, and personal information from infected systems
- Cryptocurrency Mining. Botmasters may use the combined processing power of the botnet to mine cryptocurrencies, a process known as cryptojacking
- Spreading Other Malware. Botnets can be used to distribute other types of malware, such as ransomware or spyware, to additional victims
Keylogger
A keylogger is a type of malicious software (malware) or hardware device designed to record every keystroke made on a computer or mobile device. This information is then transmitted to a third party, typically without the user’s knowledge or consent. Keyloggers are used primarily to steal sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, and other personal data.

Here you can see an example of how this virus works. As a result of its operation, the attacker can get all the keystrokes of the victim, and often in addition to that the copied and pasted information
Phishing
Although phishing is not a virus, I could not help but mention it, because through social engineering and this method, many users are hacked daily.
Phishing is a type of cyberattack in which attackers use social engineering and false representations to trick users into obtaining sensitive information such as passwords, logins, credit card numbers, and other personal information. The term comes from the word “fishing,” as phishing attacks seek to “catch” (or trick) users.
Key characteristics of phishing:
- False notifications and messages: Attackers send emails, SMS messages or social media posts pretending to be legitimate organizations to get users to provide their personal information
- Use of threats and fear: Phishers can create false scenarios, including threats of account lockout or negative consequences, to get users to react without thinking
- Fake Websites: Attackers create websites that look like legitimate websites to get users to enter their data. These websites may look very similar to the real ones, but the data entered on such websites falls into the hands of the attackers
- Social engineering: Phishers can use information from social media and other public sources to make their phishing attacks convincing



In general, the main point of phishing is to lure its victim, which is why it’s always a good idea to check the credibility of a website a thousand times before confirming anything, and not to go through sources from unreliable people.
An friend of mine who holds an honorary role on a server was hacked just like that. The attacker opened a ticket, with the help of social engineering was able to deceive the person and make him authorize his profile on a fake Discord page, and then no 2FA will help, because with your token you can enter bypassing it.
To be safe from this it just pays to be more cautious when you are logging into websites and communicating with different people. Never trust strangers, no matter how nice they may seem to you
Safety tips in WEB
The most basic things I will not describe in detail, however here are the first steps you should follow:
- Be cautious with e-mail messages. Don’t open attachments or click on links in emails from unknown senders or with suspicious attachments.
- Check the sender’s email address. Especially if you are offered something unexpected or suspicious.
- Be careful about requests for personal information. Never provide personal or financial information in response to an email, especially if it includes requests for passwords, pin numbers, or credit card numbers.
- Check website URLs. Before entering personal information or making payments, make sure you are on the right website. Fake websites can be very similar to the original.
- Use two-factor authentication (2FA). Activate two-factor authentication for an extra layer of protection for your account. This can prevent attackers from gaining access even if they recognize your password.
- Update your software. Regularly update your operating system, browsers, and other programs to address vulnerabilities that can be exploited for phishing attacks.
Now I will talk about more things that I have noticed from experience many users do not even think about, but more often than not they are the key to their security issue.
Antivirus
For some reason a lot of people don’t even think about using an antivirus, but having one increases the chance of not being infected by an intruder 95% of the time. But we have a defense system on Windows can you say? In a way this is true, but as my personal experience a few years ago showed me, it is directed solutions that deal with various viruses much better. Windows defender is much better these days, however I would advise installing other solutions, for example:
ESET NOD32

In the past, it was this antivirus that saved me a huge number of times in those situations when the windows defender simply could not recognize the virus. This solution is a paid solution and can sometimes waste a certain amount of memory on your computer, but you can feel much more confident with it. However, it is still always worth being careful! There is such a thing as a cryptor, which allows attackers to hide the presence of a virus for a certain period of time until the databases are updated for many antiviruses.
MalwareBytes
Another great utility that you can install on your computer as additional security. Unlike ESET NOD32, Windows Defender in theory will not conflict with MalwareBytes, which may play a big role in your choice

In any case, even if you are happy with windows defender, it is your responsibility to check every file when running on your computer at this source:
VirusTotal
VirusTotal is a free service that analyzes suspicious files and links (URLs) for viruses, worms, Trojans and all kinds of malware.



Antiviruses on VirusTotal do not guarantee 100% absence of malicious code in a file and do not guarantee 100% presence of malicious code in a file, as clear criteria by which software products (files) can be categorized as malicious programs have not been clearly specified anywhere so far. That’s why still you should check all of the things by yourself, be cautious!
Antivirus software developers have their own classifications and nomenclatures of malicious programs, so when checking a file, antiviruses on VirusTotal may produce different results, for example, some antiviruses will consider the file dangerous, while others will consider it safe. All antivirus databases used by the service are constantly updated. The results of the check include the dates of the latest updates of all databases. After downloading a file, the system calculates its hash and if there are results of checking a file with the same hash, it offers either to view the last analysis (indicating the date of the first and last check) or to repeat the analysis.
The service is constantly evolving, new scanners (antivirus and antitrojan) are constantly connected. VirusTotal sends suspicious files to antivirus vendors for analysis.
If you are not sure about the file you are going to install, you can upload it to this service and wait for 1 day to accurately reveal the results. Waiting is an optional procedure, but during the analysis this site may, for example, reveal that the file was protected with a cryptor and therefore did not show a threat by antiviruses.
Other Tools
There are a few other tools that are all too common, not just in crypto, but in the digital world in general, where some products stand head and shoulders above the rest in terms of safety and privacy.
Password Manager
Bitwarden is a robust password manager designed to enhance security and privacy for users.
- It offers an open-source platform, which means its code is publicly accessible for review and auditing, ensuring transparency and trust.
- Bitwarden uses end-to-end encryption, ensuring that user data is encrypted on the user’s device before being stored on Bitwarden’s servers, protecting it from potential breaches.
- It allows for optional self hosting of passwords and other data, for those technically inclined to do so.
- It’s free.

One of Bitwarden’s standout features is its support for self-hosting. This allows users to store their password vaults on their own servers, providing complete control over their data, unlike many competitors who rely solely on cloud storage. This feature is particularly appealing to privacy-conscious users who prefer non-custodial storage solutions.
Compared to competitors, Bitwarden’s open-source nature and self-hosting capability set it apart. Many other password managers, like LastPass and Dashlane, do not offer the option for users to host their own data, relying instead on proprietary, closed-source systems. While these competitors also provide strong security measures, they lack the transparency and customization options that Bitwarden offers.

Additionally, Bitwarden supports a wide range of platforms, including Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, Android, and various web browsers, ensuring seamless access across devices. With features like two-factor authentication, biometric login, and password breach monitoring, Bitwarden delivers comprehensive security, making it a top choice for those who prioritize privacy and control over their password management.
VPN
Mullvad VPN is a premier VPN service known for its robust privacy and security. It stands out by not requiring identifiable account details; rather, users generate anonymous account numbers. Mullvad also supports cryptocurrency payments, enhancing user anonymity.

Key features:
- Flat fee structure: Straightforward, affordable pricing with no hidden costs. ~$5/MO with discounts when paid in crypto.
- No sponsorships or aggressive marketing: Focused on delivering a solid core product and nothing more.
- Top-tier open-source protocols: Uses OpenVPN and WireGuard for robust security and transparency.
- Lack of Identifiable Account Information: Your Mullvad account never needs to be connected to an email, phone number, or any other identifiable piece of information.
- Sweden Based: Benefits from a country known for its strong stance on protecting universal privacy principles. (They were the ones that did all they could to protect the original PirateBay from international authorities.)
Mullvad’s commitment to privacy, clear pricing, and lack of marketing gimmicks make it superior to many competitors. Its use of trusted open-source protocols ensures a secure and reliable service, making Mullvad an excellent choice for those prioritizing genuine privacy and security.
Browser Choice
Due to a number of factors, mainly surrounding malicious ads and pop-ups, but also just for your own quality of life, I highly recommend you use either Brave with most privacy settings enabled, or if you’re a real privacy and open source nut, Firefox with u-block origin and other scripts/plugins that ensure real privacy and protection from ads as you navigate the web. This isn’t as important, as common sense can account for much of the protection offered by these things, however, it never hurts to just remove the possibility of a screw up entirely.
Conclusion
The most important tip to avoid becoming a victim of an abuser is to re-check and distrust! No matter how good a person may seem to you, he or she may just be deceiving you with the help of social engineering. Follow links only from sources you trust, learn new types of hacks as well as viruses, and be careful! Any file you download from YouTube and social networks may also be infected and you may not even realize it. The most ideal is to use several tools for different work, for example for your daily pastime one computer and for different things related to cryptocurrency another, however not everyone has that much money for these things. Stay alert!
If you found this helpful, give me a follow on Twitter (X 🤮) and let me know if you want to see more content like this! https://x.com/cimpals
https://twitter.com/cimpals
