Introduction
The dYdX community has shifted the role of the DYDX token, turning it from a mere governance token in its previous iteration, dYdX v3, into a multi-functional Layer 1 (L1) token within the new dYdX Chain. This standalone Proof-of-Stake blockchain network harnesses the DYDX token for staking, thereby contributing to the network’s security and governance. Trading on the dYdX Chain now operates without gas fees, with only maker and taker trading fees in USDC applied.
Understanding the dYdX Chain
The dYdX Chain is built using the Cosmos SDK and leverages CometBFT for consensus, requiring a robust L1 token. The dYdX community, through a series of governance votes, has confidently chosen DYDX for this vital role. All protocol-collected fees, including trading and gas fees, are distributed to Validators and Stakers, ensuring a steady rewards mechanism and aligning interests across the network.
Diving into DYDX Chain DYDX
Initially a governance token in dYdX v3, the DYDX token has undergone a transformation. September 2023 saw the community vote to adopt DYDX as the L1 token of the dYdX Chain, establishing it as a key player in network security and governance. Detailed processes and smart contracts have been put in place to facilitate the migration of the ethDYDX token from Ethereum to the dYdX Chain, though users are cautioned to approach interaction with these contracts with adequate knowledge and care.
Expanding Utility of DYDX on dYdX Chain
DYDX’s utility within the dYdX Chain is represented in staking, security, and governance.
Staking: Holders can become Validators or delegate their stake, playing a crucial role in network security and consensus. Validators are tasked with numerous responsibilities, from maintaining an in-memory orderbook to participating in block validation and governance. All network fees are distributed to Validators and Stakers, incentivizing network participation and adherence to protocol rules.
Security: As a PoS network, the dYdX Chain’s security is heavily dependent on its Validators. A diverse and robust set of Validators, backed by substantial staking, fortifies the network against potential attacks and malicious activities. However, staking is not without its risks, with slashing parameters in place to penalize detrimental behavior.
Governance: On the dYdX Chain, governance has been made more accessible, with proposals no longer requiring proposing power but rather a minimum deposit. The voting process has been simplified, though it remains a staked-DYDX-only activity.
Token Comparison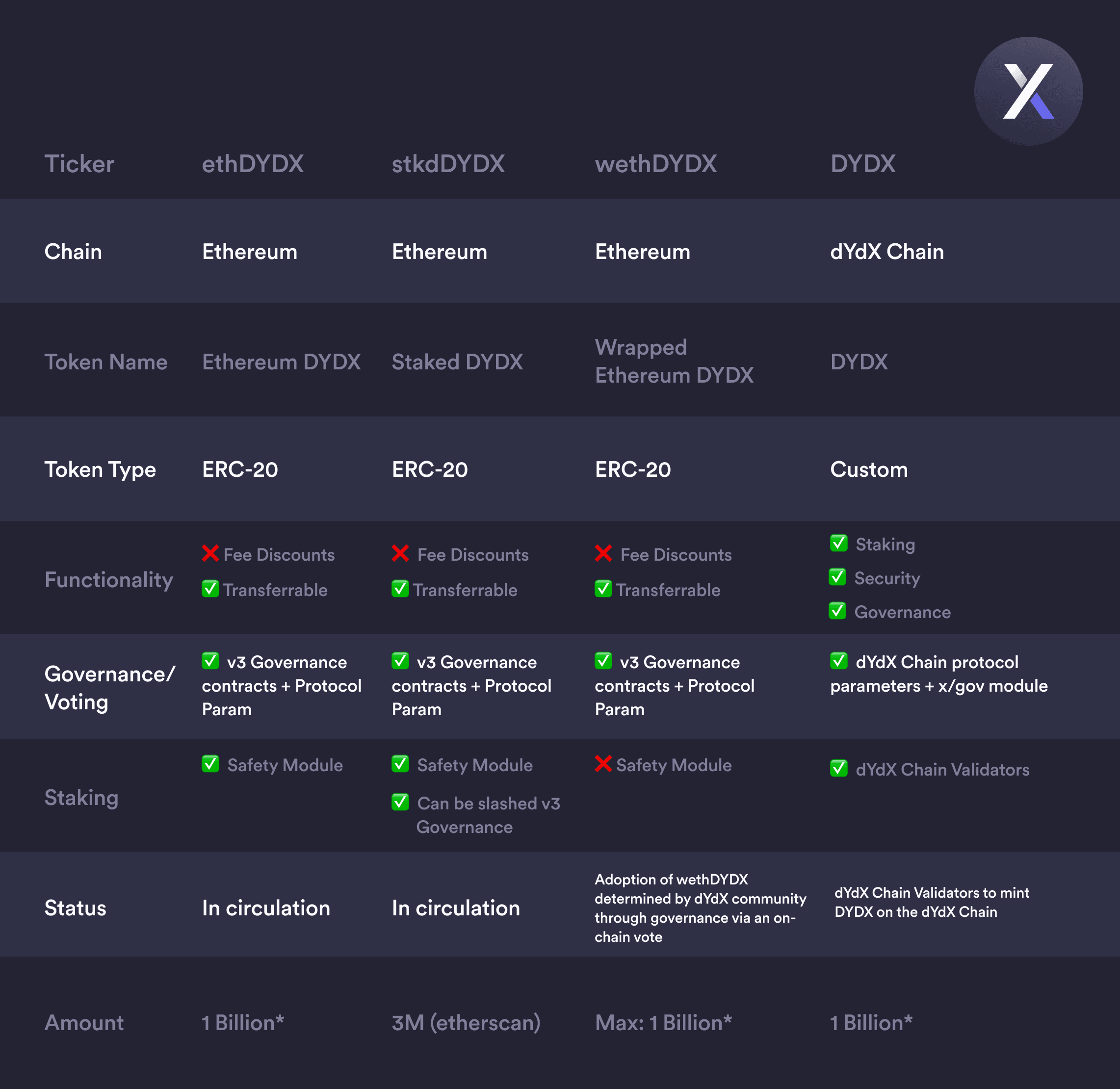

From the above chart, it’s evident that while all tokens function on the Ethereum chain, except for DYDX which is on the dYdX Chain, they have different purposes and functionalities. The ethDYDX, stkdDYDX, and wethDYDX are all ERC-20 tokens, which means they comply with the standards of the Ethereum network. The DYDX token, on the other hand, is a custom token that functions on the dYdX Chain and seems to be more versatile in terms of its functionality, especially in governance and staking.
With the dYdX Chain’s genesis, understanding the evolving mechanics of the DYDX token becomes crucial. From its roots as a governance token in dYdX v3 to its new role as a multi-functional L1 token, DYDX is poised to play a vital part in the ongoing security, governance, and functionality of the dYdX Chain.