Introduction
IOTA, a cryptocurrency that emerged in 2015 with a unique approach to distributed ledger technology, has recently made headlines with its expansion in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). It is important to note that this was first reported by Reuters only ~17 hours ago, and we have been unable to find any additional confirmation of the information reported within at the time of writing.
IOTA’s Background and Technological Framework
Distinct from conventional blockchain technology, IOTA is designed to facilitate transactions in the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem. Using a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) called the Tangle, it allows for feeless transactions and lower resource needs, which is advantageous for IoT applications. Historically, IOTA’s journey has been marked by both innovation and various challenges, including governance and security issues.
Recent Developments in the UAE
IOTA’s foray into the UAE, marked by the inauguration of the IOTA Ecosystem DLT Foundation, represents a significant strategic expansion. This new entity, fueled by a $100 million investment in IOTA tokens, is positioned to foster the IOTA ecosystem and expedite the development of its technology. The foundation is set to collaborate with institutional entities, governments, and academic institutions. A key focus of this collaboration is the tokenization of tangible assets, converting them into digital tokens on the blockchain. This process, which could revolutionize the handling of asset ownership, aligns well with the UAE’s vision of becoming a hub for blockchain innovation.
Market Reaction and Price Fluctuations
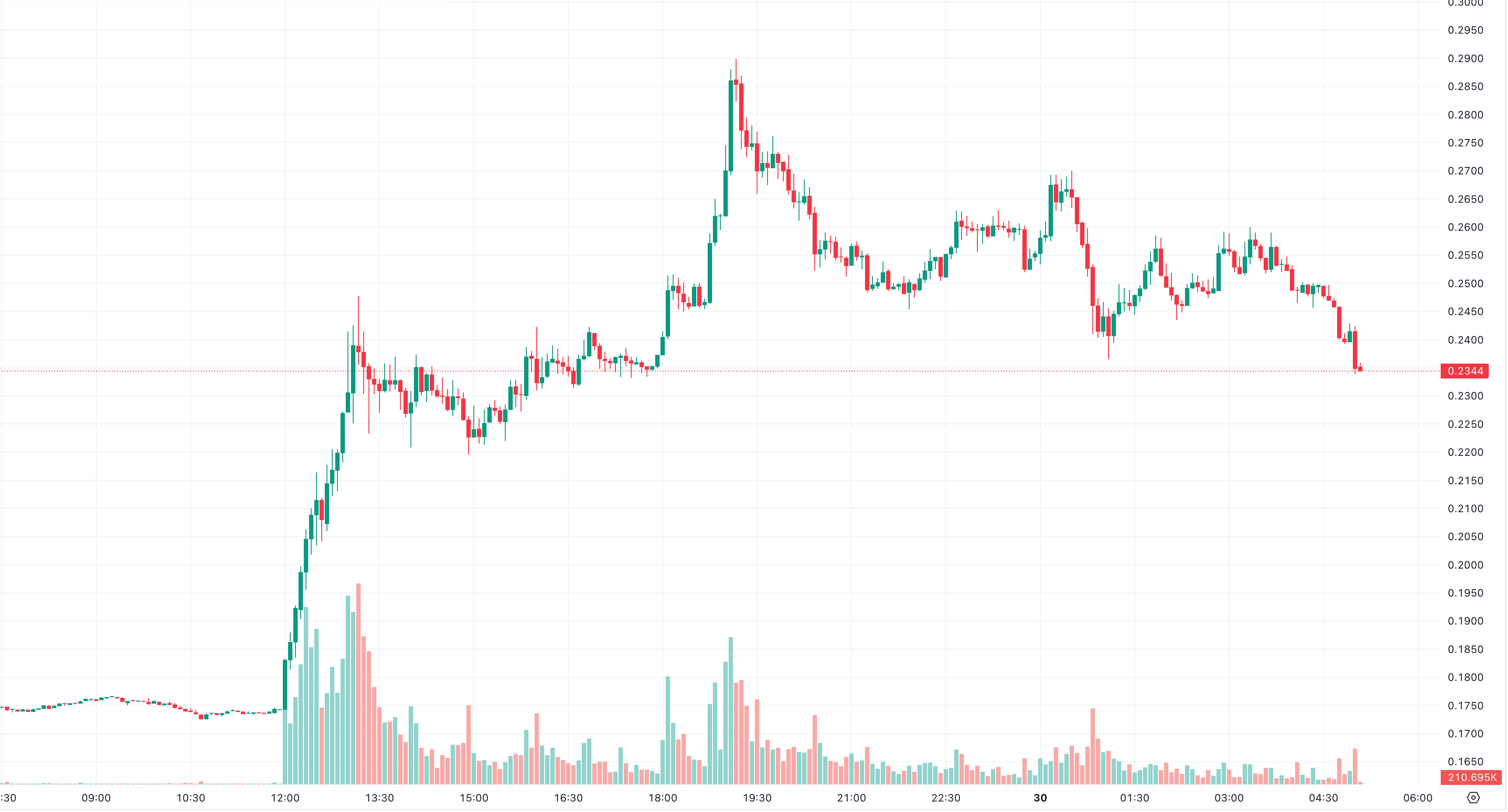
Following this announcement, there was a notable increase in IOTA’s token price, rising from $0.174 to $0.228 within an hour. At peak, it saw ~$0.29, and as of now, 12:00 EST, it’s price sits at $0.2414 This price movement was, of course, accompanied by a spike in trading volume. However, the market response also included quick profit-taking, indicating a cautious approach by some investors and traders, possibly due to being unable get any additional information on the news at this time.
IOTA’s Position in a Global Context
IOTA’s venture in the UAE reflects a strategic alignment with the region’s progressive approach to digital currencies. This contrasts with the regulatory uncertainties IOTA has faced in European markets. By situating itself in the UAE, IOTA benefits from a regulatory environment that is not only receptive to blockchain technology but also actively encourages its development. This move could serve as a model for other crypto ventures looking to navigate the complex global regulatory landscape. The UAE’s positioning as a forward-thinking digital economy could offer IOTA the stability and support necessary for its long-term growth and innovation in the blockchain domain.
Potential Challenges and Future Outlook
The long-term impact of IOTA’s ventures in the UAE and its overall market performance will likely hinge on a variety of factors, including adherence to regulatory standards, technological advancements, and broader market trends. The current market enthusiasm, while notable, should be viewed within the larger context of the typically volatile nature of cryptocurrency markets.
Final Remarks
As IOTA extends its reach into new territories with the foundation in Abu Dhabi, its unique technological underpinnings, particularly the Tangle, come into focus. The Tangle, a novel approach diverging from traditional blockchain, allows for simultaneous transactions, enhancing scalability and efficiency, particularly for IoT applications. This innovation, along with feeless transactions and low energy requirements, positions IOTA distinctively in the blockchain landscape.
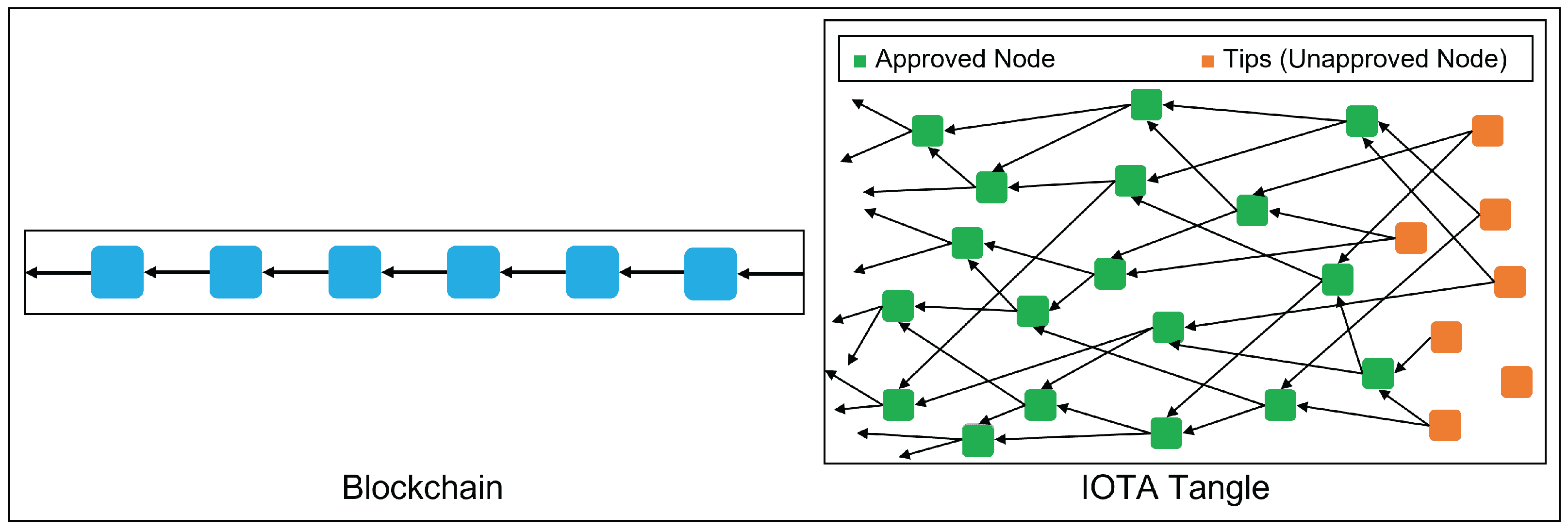
IOTA’s progress in the UAE offers a glimpse into how innovative blockchain technologies can adapt and thrive in different regulatory environments. It also highlights the evolving nature of digital currencies, where pioneering technology like IOTA’s Tangle intersects with complex regulatory frameworks to shape the future of digital transactions and asset management.