Introduction
Double signing, also known as equivocation, is a serious offense in the world of blockchain technology. It occurs when a validator, who is responsible for verifying and adding new transactions to the blockchain, signs two different blocks at the same height (i.e., position in the blockchain). This is akin to a notary public signing two conflicting documents, hence the term “double signing.”
How Double Signing Occurs
Double signing can occur unintentionally due to technical issues such as network latency or software bugs. However, it can also be a deliberate act aimed at manipulating the blockchain for personal gain. For instance, a validator might attempt to double sign to create a fork in the blockchain, allowing them to spend the same cryptocurrency twice (a “double-spend” attack).
Consequences of Double Signing
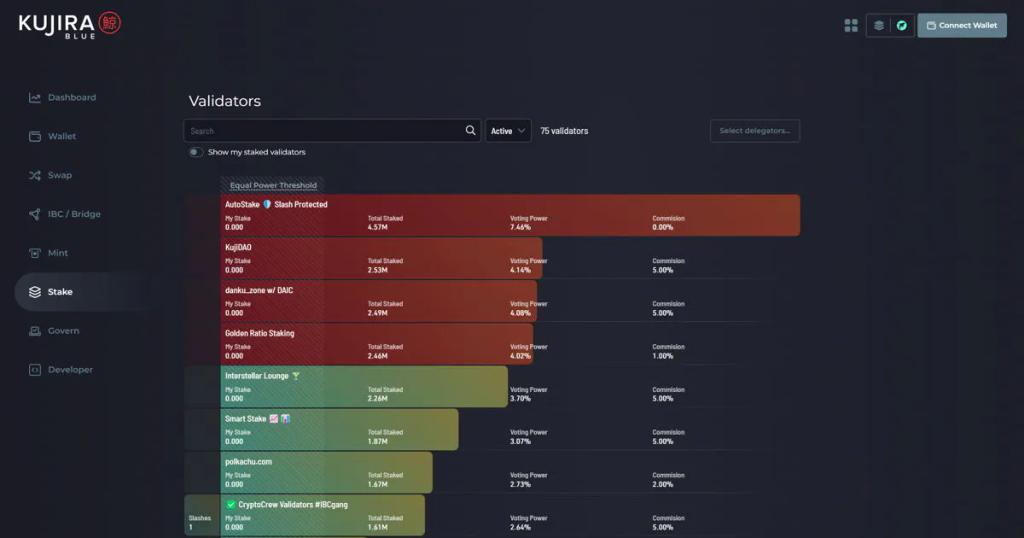
The consequences of double signing are severe. In Proof of Stake